GLP-1 and GIP Receptors: How They Work and Support Weight Loss with Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
The quest for effective weight loss solutions has led to groundbreaking discoveries in metabolic science, notably in the role of specific hormones and receptors within the body. Among these, GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) and GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide) receptors have been identified as key players in managing weight, blood glucose, and metabolic health. Two medications—semaglutide and tirzepatide—target these receptors to deliver powerful effects on appetite control and glucose regulation, making them effective tools for weight loss.
In this guide, we'll explore:
- How GLP-1 and GIP receptors work in the body.
- How activating these receptors promotes weight loss.
- The mechanisms of semaglutide and tirzepatide in working with these receptors.
- Key benefits, side effects, and usage guidelines for these medications.
Let’s dive into the science of GLP-1 and GIP receptors and see how semaglutide and tirzepatide can be transformative for weight loss and overall metabolic health.
1. Understanding GLP-1 and GIP Receptors: Key to Metabolic Control
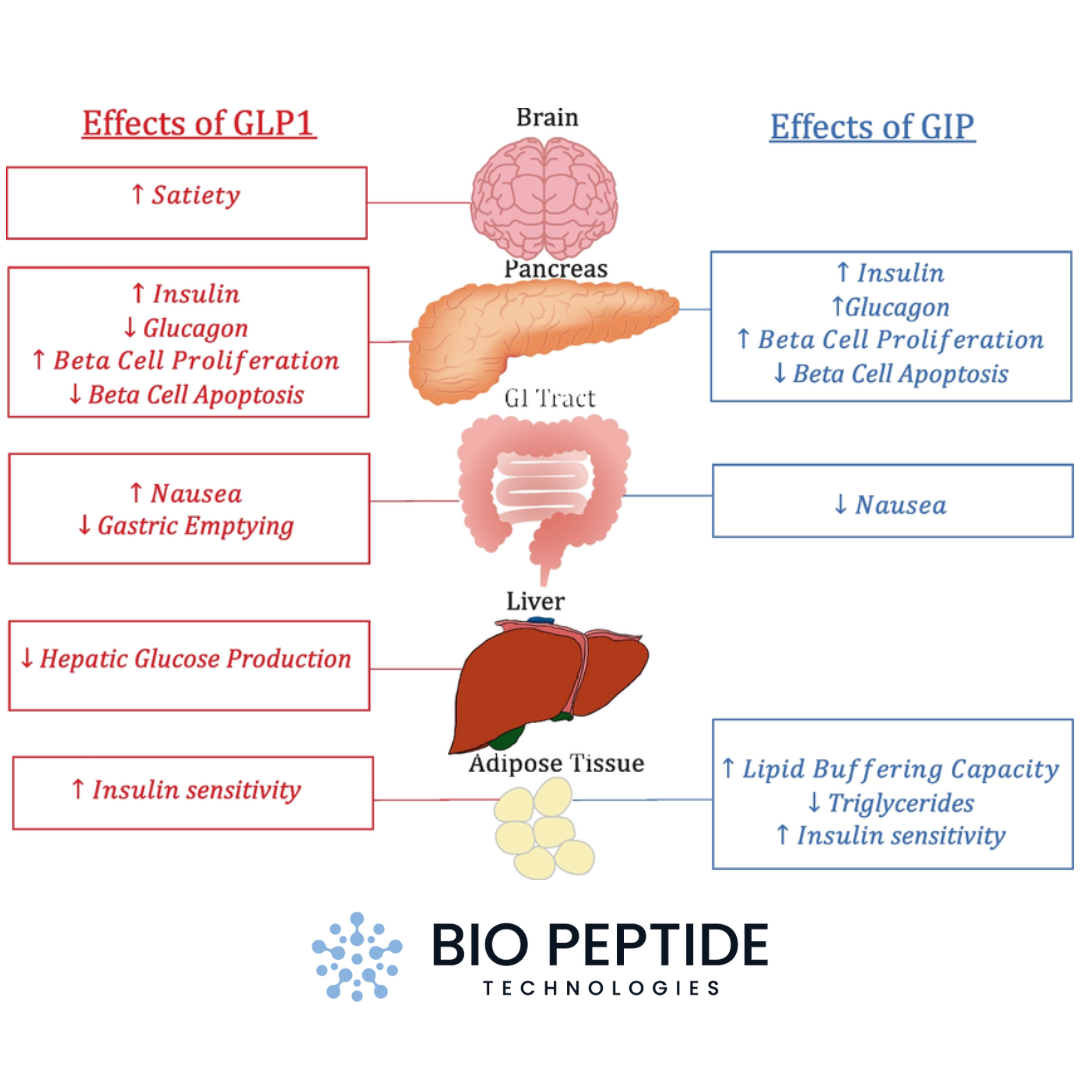
Both GLP-1 and GIP are hormones known as incretins, naturally produced in the gut. These hormones play a major role in managing how the body processes food, manages blood sugar, and controls appetite.
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1): Released from the intestines when food is consumed, GLP-1 helps regulate insulin secretion, slow gastric emptying (meaning food moves more slowly through the stomach), and increase feelings of fullness.
- GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide): Produced by the small intestine in response to eating, GIP promotes insulin secretion and, like GLP-1, also helps manage blood sugar levels.
The receptors for these hormones are found throughout the body—in the pancreas, brain, stomach, and other areas critical to metabolism. When activated, these receptors help coordinate metabolic responses, making GLP-1 and GIP essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and regulating appetite.
The Role of GLP-1 and GIP Receptors in Weight Management
By interacting with these receptors, GLP-1 and GIP influence several processes that make weight management more achievable:
- Enhancing Satiety: Both GLP-1 and GIP receptors act in the brain’s hypothalamus, a region responsible for hunger regulation, helping to reduce the desire to eat.
- Slowing Digestion: Activation of GLP-1 receptors slows gastric emptying, keeping food in the stomach longer and prolonging the sensation of fullness.
- Insulin Secretion and Glucose Control: Both GLP-1 and GIP enhance insulin secretion in response to glucose, ensuring blood sugar remains stable after meals and reducing cravings caused by sugar dips.
2. How GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Activation Supports Weight Loss
Research has shown that individuals who struggle with weight often have reduced responsiveness to GLP-1 and GIP. By administering medications that mimic or enhance these hormones, weight loss becomes more achievable.
Here’s how GLP-1 and GIP receptor activation works to support weight loss:
Appetite Reduction and Fullness Enhancement
GLP-1 and GIP receptors in the brain play a direct role in controlling appetite. When GLP-1 and GIP levels increase, signals are sent to the brain to reduce feelings of hunger. This process is especially important for individuals with obesity, as studies show they often experience heightened hunger signals and reduced fullness after meals. Medications that increase GLP-1 and GIP activity can correct these imbalances, making it easier to consume fewer calories.
Slowing Gastric Emptying
Gastric emptying is the process by which food leaves the stomach and enters the intestines. Faster gastric emptying often leads to increased hunger shortly after meals. GLP-1 delays this process, allowing food to stay in the stomach longer, which prolongs the sensation of fullness. This reduced hunger can lead to smaller portions and fewer cravings for high-calorie snacks.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Control
The insulin-regulating effects of GLP-1 and GIP are vital for managing blood sugar levels. When blood sugar spikes after a meal, GLP-1 and GIP receptors stimulate insulin release, lowering blood sugar to a stable level. By enhancing these effects, GLP-1 and GIP medications help reduce insulin resistance, which is often a contributor to obesity. Improved insulin sensitivity helps prevent the “blood sugar rollercoaster,” which is often associated with hunger spikes and cravings.
3. How Semaglutide Works with GLP-1 Receptors
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, meaning it binds to GLP-1 receptors and activates them in a similar way to the body’s natural GLP-1 hormone. Available under the brand names Ozempic and Wegovy, semaglutide has gained popularity for its dual effectiveness in managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss.
Mechanism of Action: How Semaglutide Enhances GLP-1 Activity
- Mimicking GLP-1 Activity: Semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors in the pancreas, brain, and stomach, effectively mimicking natural GLP-1 hormone. This leads to enhanced insulin secretion and reduced glucagon release, helping stabilize blood glucose levels.
- Suppressing Appetite: In the brain, semaglutide’s action on GLP-1 receptors helps decrease appetite, reducing the drive to eat excessively.
- Slowing Gastric Emptying: By delaying how quickly food exits the stomach, semaglutide prolongs fullness and helps prevent overeating.
Semaglutide in Clinical Use: Weight Loss and Diabetes Management
Studies have shown that semaglutide can lead to significant weight loss when combined with lifestyle changes. In clinical trials, people using semaglutide experienced an average weight reduction of 10-15%, which is higher than many traditional weight loss medications.
Benefits of Semaglutide:
- Reduced hunger and enhanced fullness.
- Stabilized blood sugar levels, especially useful for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Improved cardiovascular outcomes in people with diabetes, lowering the risk of heart disease.
Possible Side Effects of Semaglutide
Some users may experience nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly when first starting treatment. These side effects often subside as the body adjusts, and they can be managed by gradually increasing the dosage.
4. How Tirzepatide Works with Both GLP-1 and GIP Receptors
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is unique in that it acts as a dual agonist, targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. By activating both incretin pathways, tirzepatide provides an even more comprehensive approach to weight management and blood glucose control, offering promising results beyond what single GLP-1 receptor activation can achieve.
Mechanism of Action: How Tirzepatide Activates GLP-1 and GIP Receptors
- Dual Receptor Activation: Tirzepatide binds to both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, and helping the body use glucose more efficiently.
- Enhanced Appetite Control: The dual receptor approach intensifies appetite suppression, with effects in the brain that decrease hunger signals and prolong satiety.
- Superior Weight Loss Results: The combined action of GLP-1 and GIP receptors contributes to more significant reductions in weight by enhancing the body’s natural mechanisms for controlling hunger and energy storage.
Tirzepatide in Clinical Use: Superior Weight Loss Outcomes
Studies have shown that tirzepatide can produce greater weight loss results than GLP-1 agonists alone. In trials, tirzepatide users achieved weight loss of up to 20% of their body weight, surpassing results seen with semaglutide. Additionally, tirzepatide’s impact on insulin sensitivity makes it especially valuable for people with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Benefits of Tirzepatide:
- Greater reductions in appetite and calorie intake.
- Enhanced glucose control through dual action on GLP-1 and GIP receptors.
- Higher rates of weight loss compared to single-receptor GLP-1 agonists.
- Potential benefits for cardiovascular health due to comprehensive metabolic improvements.
Possible Side Effects of Tirzepatide
Similar to semaglutide, tirzepatide’s side effects may include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea and vomiting. These symptoms tend to lessen as the body adapts to the medication. Some studies suggest that tirzepatide’s dual receptor activity may make it easier to tolerate than single receptor agonists, but this can vary by individual.
5. Choosing Between Semaglutide and Tirzepatide for Weight Loss
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are effective for weight management, but choosing between them may depend on individual health factors, weight loss goals, and tolerance.
- For Those Primarily Seeking Weight Loss: Tirzepatide’s dual mechanism may offer an advantage, especially for people aiming for substantial weight loss.
- For Diabetes Management: Both medications are highly effective for blood sugar control, though tirzepatide’s additional GIP receptor activity can provide better results for some individuals with insulin resistance.
- Side Effect Tolerance: Some individuals may tolerate one medication better than the other. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing can help minimize initial side effects.
6. How to Use Semaglutide and Tirzepatide Effectively
Administration
Both medications are administered via injection:
- Semaglutide is typically injected once weekly.
- Tirzepatide is also injected once weekly, with doses titrated based on individual needs and tolerance.
Combining with Lifestyle Changes
While these medications offer powerful effects, combining them with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and behavioral changes can maximize their benefits.
7. Key Takeaways on GLP-1 and GIP Receptors, Semaglutide, and Tirzepatide
GLP-1 and GIP receptors are integral to appetite control, insulin sensitivity, and metabolic health. By targeting these receptors, semaglutide and tirzepatide offer new options for weight loss and glucose management. Their unique mechanisms make them suitable for individuals with obesity, type 2 diabetes, or metabolic syndrome who may benefit from additional metabolic support.
Summary of Benefits:
- Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptor agonist that reduces hunger, promotes weight loss, and improves blood glucose control.
- Tirzepatide: Dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist offering enhanced weight loss, improved glucose stability, and additional benefits for insulin resistance.

Leave a comment